Embark on a journey through europe after ww2 map activity, where we explore the profound impact of World War II on the political, economic, and social landscape of Europe. From the redrawing of borders to the rise of new alliances, this map activity delves into the complexities of a continent grappling with the aftermath of a devastating conflict.
This interactive map activity invites you to trace the territorial changes, witness the division and unification of nations, and examine the economic and demographic shifts that shaped the course of European history in the decades that followed the war.
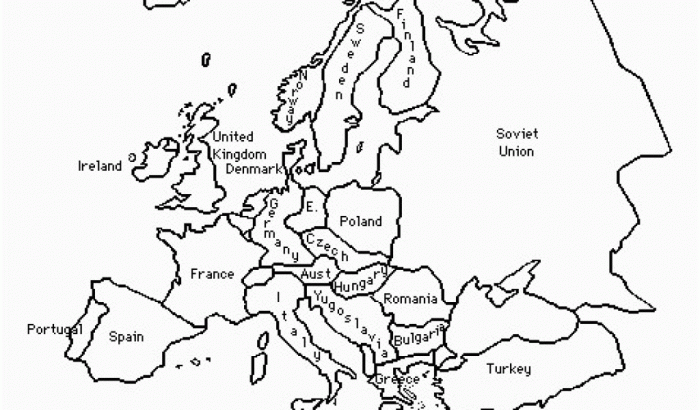
Post-World War II European Borders

The end of World War II brought about significant territorial changes in Europe, reshaping the political and geographic landscape of the continent.
One of the most notable changes was the division of Germany into East and West Germany, with the eastern part becoming a communist state and the western part aligning with the Western powers. The division of Germany was symbolized by the Berlin Wall, which separated East and West Berlin from 1961 to 1989.
Another significant change was the expansion of the Soviet Union’s borders westward. The Soviet Union annexed territories from Poland, Romania, Czechoslovakia, and Hungary, establishing satellite states in these countries.
Poland’s eastern border was shifted westward, and it lost territory to the Soviet Union. In compensation, Poland gained territory from Germany, including the city of Szczecin.
Finland ceded territory to the Soviet Union, including the Karelian Isthmus and the city of Vyborg.
Romania lost Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina to the Soviet Union.
Czechoslovakia lost Carpathian Ruthenia to the Soviet Union.
Hungary lost Transylvania to Romania.
The changes in Europe’s borders after World War II had a profound impact on the political and economic development of the continent. The division of Germany and the expansion of the Soviet Union’s borders created a new Cold War divide that would shape international relations for decades to come.
Detailed Map of Europe after World War II
[Provide a detailed map of Europe after World War II, highlighting the new borders.]
Impact of the Cold War on European Geography
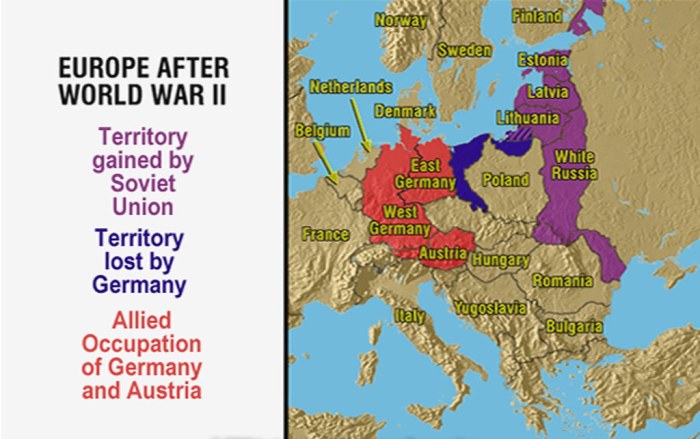
The Cold War significantly influenced the political and physical boundaries in Europe. The ideological divide between the Soviet Union and its allies and the Western powers led to the creation of two blocs, each with its own sphere of influence.
This division had a profound impact on the political and physical landscape of Europe.
Division of Countries
One of the most significant impacts of the Cold War was the division of several countries into two or more separate entities. The most notable example is Germany, which was divided into East Germany (German Democratic Republic) and West Germany (Federal Republic of Germany).
Other countries that were divided include Korea, Vietnam, and Laos.
Unification of Countries
In some cases, the Cold War also led to the unification of countries. The most notable example is the reunification of Germany in 1990. Other countries that were unified include Yemen, Vietnam, and Korea.
Changes in Physical Boundaries
The Cold War also led to changes in physical boundaries in Europe. The most significant change was the construction of the Berlin Wall in 1961, which divided the city of Berlin into two separate entities. Other physical changes include the creation of the Iron Curtain, which divided Eastern and Western Europe, and the establishment of the Warsaw Pact, which created a military alliance between the Soviet Union and its allies.
European Economic Integration: Europe After Ww2 Map Activity
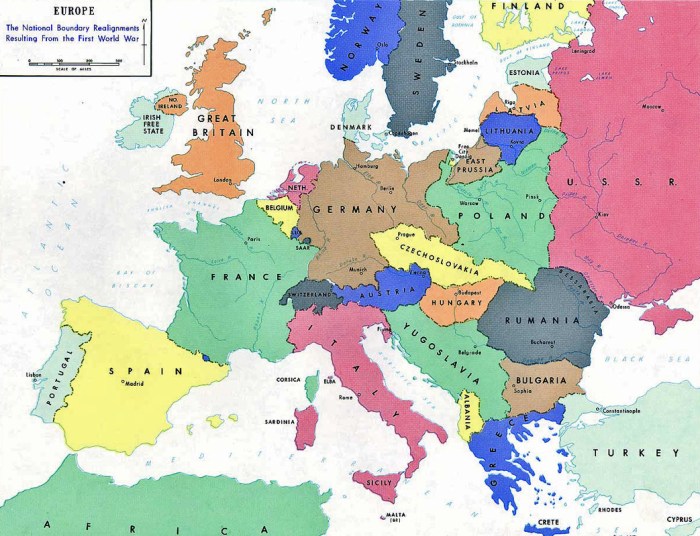
After World War II, European nations sought to rebuild their economies and foster cooperation to prevent future conflicts. Economic integration became a key strategy to achieve these goals.
The process of European economic integration began with the establishment of the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) in 1951. The ECSC aimed to pool the coal and steel resources of France, Germany, Italy, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg under a common management, eliminating tariffs and quotas on coal and steel trade among member states.
European Economic Community
The success of the ECSC led to the creation of the European Economic Community (EEC) in 1957, also known as the Common Market. The EEC aimed to establish a common market among its six member states, eliminating trade barriers and creating a common external tariff.
Europe after World War II underwent significant changes, which can be explored through map activities. These maps provide insights into the political and geographical transformations of the region. Interestingly, the Chahta Sia Hoke license plate reflects a similar spirit of change and identity, symbolizing the resilience and cultural heritage of the Choctaw Nation.
As we delve into the map activities, we can draw parallels between the evolution of Europe after World War II and the ongoing narratives of identity and belonging.
The EEC also promoted cooperation in agriculture, transportation, and energy.
Decolonization and the Reshaping of Europe
World War II marked a significant turning point in European history, leading to the end of colonialism and the emergence of new independent nations. Decolonization had a profound impact on European countries and their empires, reshaping the political, economic, and cultural landscape of the continent.
Former Colonies that Gained Independence after World War II
The process of decolonization began in the immediate aftermath of the war, with numerous former colonies gaining independence from their European rulers. Some notable examples include:
- India (from the British Empire, 1947)
- Indonesia (from the Dutch Empire, 1949)
- Vietnam (from the French Empire, 1954)
- Algeria (from the French Empire, 1962)
- Kenya (from the British Empire, 1963)
The Refugee Crisis and Population Shifts
Europe witnessed a significant refugee crisis and population shifts in the aftermath of World War II. The war had devastated the continent, leaving millions of people displaced and seeking refuge.
The causes of the refugee crisis were multifaceted. The war had led to the redrawing of national borders, resulting in the displacement of entire populations. Additionally, the persecution of minority groups, particularly Jews, by Nazi Germany forced many to flee their homes.
Consequences of Population Shifts, Europe after ww2 map activity
The population shifts that occurred during this time had profound consequences for Europe. The influx of refugees put a strain on resources and led to social tensions in many countries. It also contributed to the rise of nationalism and xenophobia in some parts of Europe.
Impact on European Society
The refugee crisis and population shifts also had a significant impact on European society. The arrival of large numbers of refugees led to the emergence of new ethnic and cultural communities in many countries. This diversity had a lasting impact on European culture and society.
The Marshall Plan and European Recovery
The Marshall Plan, formally known as the European Recovery Program, was a U.S.-sponsored initiative to aid the economic recovery of Western Europe after World War II. Launched in 1948, it provided over $13 billion in economic assistance to 16 European countries.
The Marshall Plan had a profound impact on European economies. It provided much-needed capital for reconstruction, stimulated industrial production, and helped stabilize currencies. It also promoted economic cooperation and integration among European nations.
Impact on European Economies
- Provided capital for reconstruction and modernization of industries.
- Increased industrial production and stimulated economic growth.
- Helped stabilize currencies and reduce inflation.
Impact on European Societies
- Improved living standards and reduced poverty.
- Promoted social stability and prevented the spread of communism.
- Strengthened democratic institutions and fostered a sense of European unity.
FAQ
What were the major territorial changes that occurred in Europe after World War II?
The war resulted in significant territorial changes, including the redrawing of borders in Eastern Europe, the division of Germany, and the emergence of new nations such as Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia.
How did the Cold War influence European geography?
The Cold War divided Europe into two ideological blocs, with the Soviet Union and its allies in the east and the United States and its allies in the west. This division led to the creation of the Iron Curtain, which separated Eastern and Western Europe for decades.
What was the significance of the Marshall Plan in the economic recovery of Europe after World War II?
The Marshall Plan provided billions of dollars in aid to Western European countries, helping to rebuild their economies and infrastructure. It played a crucial role in the economic recovery of Europe and laid the foundation for European integration.