Rank the following elements by increasing electronegativity – Electronegativity, a fundamental chemical property, measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons. This comprehensive guide explores the concept of electronegativity, its periodic trends, measurement methods, applications, and exceptions. Understanding electronegativity is crucial for predicting bond polarity, chemical reactivity, and molecular structure, providing valuable insights into the behavior of elements and compounds.
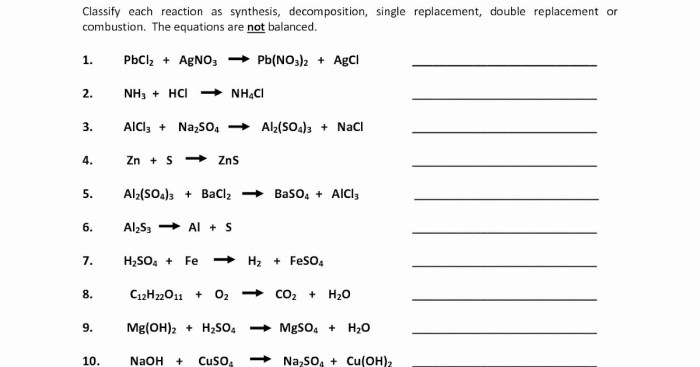
Electronegativity: Definition and Overview: Rank The Following Elements By Increasing Electronegativity

Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. It is a fundamental property of elements that influences their chemical behavior and reactivity.
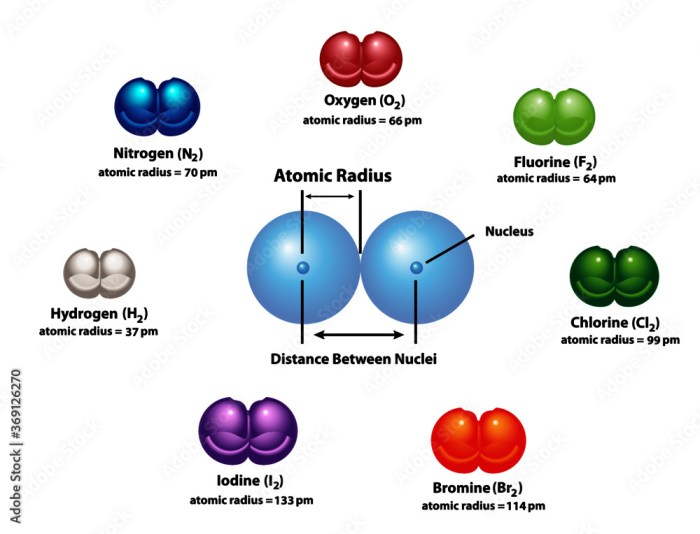
Electronegative elements have a strong tendency to attract electrons towards themselves, while electropositive elements have a weak tendency to do so. Some examples of electronegative elements include fluorine, oxygen, and chlorine, while electropositive elements include sodium, potassium, and calcium.
Electronegativity generally increases across a period from left to right and decreases down a group in the periodic table. This trend is due to the increase in atomic number and decrease in atomic radius, respectively.
Periodic Trends in Electronegativity
The following table shows the electronegativity values of elements in each group and period:
| Group | Period 1 | Period 2 | Period 3 | Period 4 | Period 5 | Period 6 | Period 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H (2.2) | Li (1.0) | Na (0.9) | K (0.8) | Rb (0.8) | Cs (0.7) | Fr (0.7) |
| 2 | – | Be (1.5) | Mg (1.2) | Ca (1.0) | Sr (1.0) | Ba (0.9) | Ra (0.9) |
| 3 | – | B (2.0) | Al (1.6) | Ga (1.6) | In (1.7) | Tl (1.8) | – |
| 4 | – | C (2.5) | Si (1.8) | Ge (1.8) | Sn (1.9) | Pb (2.0) | – |
| 5 | – | N (3.0) | P (2.1) | As (2.0) | Sb (1.9) | Bi (1.9) | – |
| 6 | – | O (3.5) | S (2.5) | Se (2.4) | Te (2.1) | Po (2.0) | – |
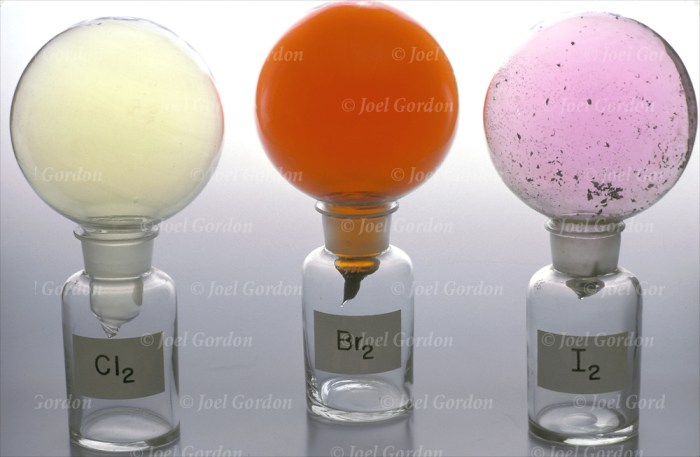
| 7 | – | F (4.0) | Cl (3.0) | Br (2.8) | I (2.5) | At (2.2) | – |
As can be seen from the table, electronegativity generally increases across a period from left to right and decreases down a group. This trend is due to the increase in atomic number and decrease in atomic radius, respectively.
Methods for Measuring Electronegativity, Rank the following elements by increasing electronegativity
There are several different methods for measuring electronegativity. Two of the most common methods are the Pauling scale and the Mulliken scale.
The Pauling scale is based on the energy difference between the ionization energy and the electron affinity of an atom. The Mulliken scale is based on the average of the ionization energy and the electron affinity of an atom.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. The Pauling scale is simple to use and can be applied to a wide range of elements. However, it does not take into account the polarizability of atoms. The Mulliken scale is more accurate but it is more difficult to use and cannot be applied to all elements.
Applications of Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a useful concept that can be used to explain a wide range of chemical phenomena. For example, electronegativity can be used to:
- Determine the polarity of bonds
- Predict the chemical reactivity of elements
- Explain the properties of compounds
For example, the electronegativity of fluorine is 4.0, while the electronegativity of sodium is 0.9. This difference in electronegativity means that fluorine will tend to attract electrons away from sodium in a chemical bond, resulting in a polar bond.
Electronegativity and Molecular Structure
Electronegativity also plays an important role in determining the molecular structure of compounds. For example, the electronegativity of carbon is 2.5, while the electronegativity of hydrogen is 2.1. This difference in electronegativity means that carbon will tend to attract electrons away from hydrogen in a C-H bond, resulting in a polar bond.
The polarity of the C-H bond affects the overall molecular structure of a compound. For example, in methane (CH 4), the four C-H bonds are all polar, resulting in a tetrahedral molecular structure.
Clarifying Questions
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond.
Which element has the highest electronegativity?
Fluorine has the highest electronegativity among all elements.
How does electronegativity affect chemical bonding?
Electronegativity differences between atoms determine the polarity of chemical bonds, influencing their strength and reactivity.