Suggest reagents that would achieve the following transformation sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Delve into the intricacies of reagent selection, reaction optimization, byproduct management, and safety considerations as we embark on a journey to uncover the reagents that will lead to the desired transformation.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Reagent Identification: Suggest Reagents That Would Achieve The Following Transformation
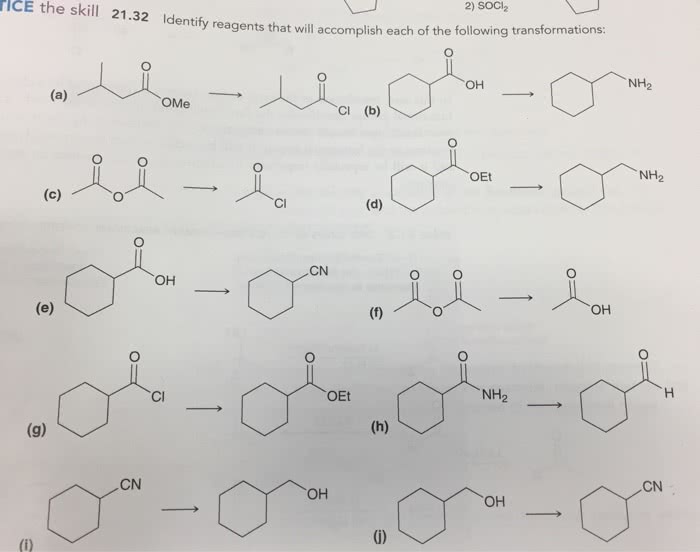
Selecting appropriate reagents for a desired transformation involves careful consideration of several criteria. The reagents should:
- Be compatible with the functional groups present in the starting material.
- Possess the necessary reactivity to facilitate the desired transformation.
- Exhibit high selectivity to minimize the formation of unwanted byproducts.
A comprehensive list of potential reagents and their respective mechanisms of action can be found in the literature. Factors influencing reagent selectivity and efficiency include:
- Steric effects
- Electronic effects
- Solvent effects
Reaction Optimization

Optimizing the reaction yield and selectivity involves carefully controlling the experimental conditions. The following factors play a crucial role:
Catalysts, Suggest reagents that would achieve the following transformation
Catalysts can significantly enhance the reaction rate and selectivity by providing an alternative pathway with a lower activation energy. The choice of catalyst depends on the specific transformation and the substrate.
Solvents
Solvents can influence the reaction rate, selectivity, and solubility of the reactants and products. The solvent should be inert and compatible with the reagents and reaction conditions.
Temperature
Temperature can affect the reaction rate and equilibrium. The optimal temperature depends on the specific transformation and the stability of the reactants and products.
Monitoring the reaction progress is essential for determining the optimal reaction endpoint. Techniques such as thin-layer chromatography (TLC), gas chromatography (GC), or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) can be used for this purpose.
Byproduct Management
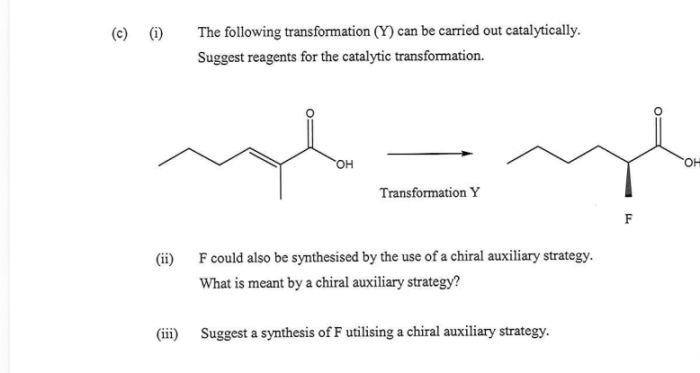
Side reactions and byproduct formation are common challenges in organic synthesis. To minimize byproduct formation, several strategies can be employed:
- Using selective reagents that minimize unwanted reactions.
- Employing scavengers to trap reactive intermediates or byproducts.
- Protecting sensitive functional groups to prevent unwanted reactions.
Isolating the desired product from byproducts can be achieved through techniques such as:
- Extraction
- Chromatography
- Crystallization
Safety Considerations
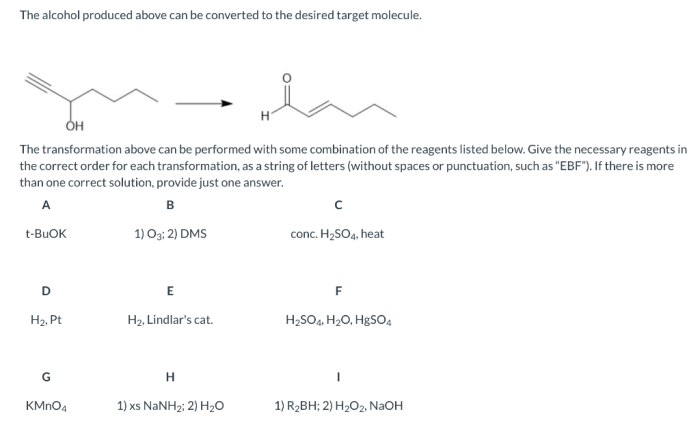
Handling and storing chemicals in a laboratory setting require strict adherence to safety protocols. Potential hazards associated with the reagents and reaction conditions must be identified and addressed.
Safety protocols include:
- Proper ventilation to prevent inhalation of toxic fumes.
- Wearing appropriate protective gear, such as gloves, goggles, and a lab coat.
- Following established procedures for handling and disposal of chemicals.
In case of an emergency, it is crucial to have a plan in place and to know the location of safety equipment, such as fire extinguishers and eyewash stations.
Key Questions Answered
What factors influence reagent selectivity and efficiency?
Reagent selectivity and efficiency are influenced by factors such as the electronic properties of the reactants, steric effects, solvent effects, and reaction temperature.
How can byproduct formation be minimized?
Byproduct formation can be minimized through strategies such as using scavengers, protecting groups, and optimizing reaction conditions to favor the desired product.
What safety protocols should be followed when handling reagents?
When handling reagents, it is essential to follow safety protocols such as proper ventilation, wearing protective gear, and being aware of the potential hazards associated with the chemicals.